Hyunseo Kim (김현서)
I am a PhD student in Interdisciplinary program in Neuroscience at Seoul National University, and a member of the biointelligence laboratory led by Byoung-Tak Zhang.
Reseach interest: Robotics, Computer Vision, 3D Vision in Robotics
Email : hskhexasu@snu.ac.kr | hyunseo.kim159@gmail.com
CV / Google Scholar / Github / LinkedIn
I am a PhD student in Interdisciplinary program in Neuroscience at Seoul National University, and a member of the biointelligence laboratory led by Byoung-Tak Zhang.
Reseach interest: Robotics, Computer Vision, 3D Vision in Robotics
Email : hskhexasu@snu.ac.kr | hyunseo.kim159@gmail.com
CV / Google Scholar / Github / LinkedIn
[2023/11] Our paper on Learning Object Motion and Appearance Dynamics with Object-Centric Representations is accepted at CRL workshop in NeurIPS 2023.
[2023/08] I joined C51 as a part-time research enginner.
[2023/01] Our paper on Exit-aware Object Tracker for Safe Robotic Manipulation of Moving Object is accepted at ICRA 2023.
[2022/09] Our paper on Robust Imitation via Mirror Descent Inverse Reinforcement Learning is accepted at NeurIPS 2022.
[2022/07] Our team Tidyboy won 2nd place in the Domestic Standard Platform competition at Robocup@Home 2022, which was held in Thailand. 🏆
[2023/08] I joined C51 as a part-time research enginner.
[2023/01] Our paper on Exit-aware Object Tracker for Safe Robotic Manipulation of Moving Object is accepted at ICRA 2023.
[2022/09] Our paper on Robust Imitation via Mirror Descent Inverse Reinforcement Learning is accepted at NeurIPS 2022.
[2022/07] Our team Tidyboy won 2nd place in the Domestic Standard Platform competition at Robocup@Home 2022, which was held in Thailand. 🏆
*Authors contributed equally
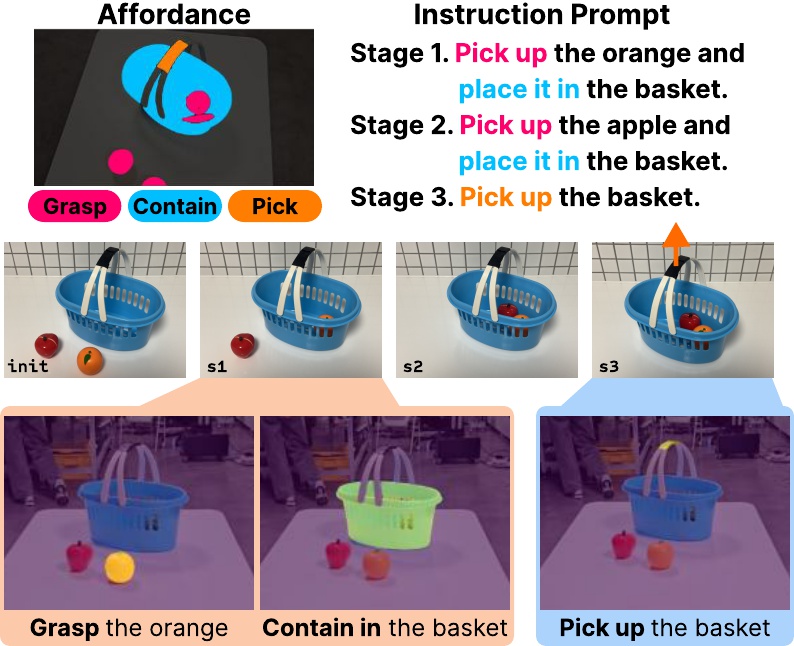
AffoRo-GS: Few-shot 3D Affordance Learning for Open-vocabulary Robotic Manipulation with Gaussian Splatting
Hyunseo Kim, Yeon-Ji Song, Minsu Lee and Byoung-Tak Zhang
Under review at IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters
Hyunseo Kim, Yeon-Ji Song, Minsu Lee and Byoung-Tak Zhang
Under review at IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters
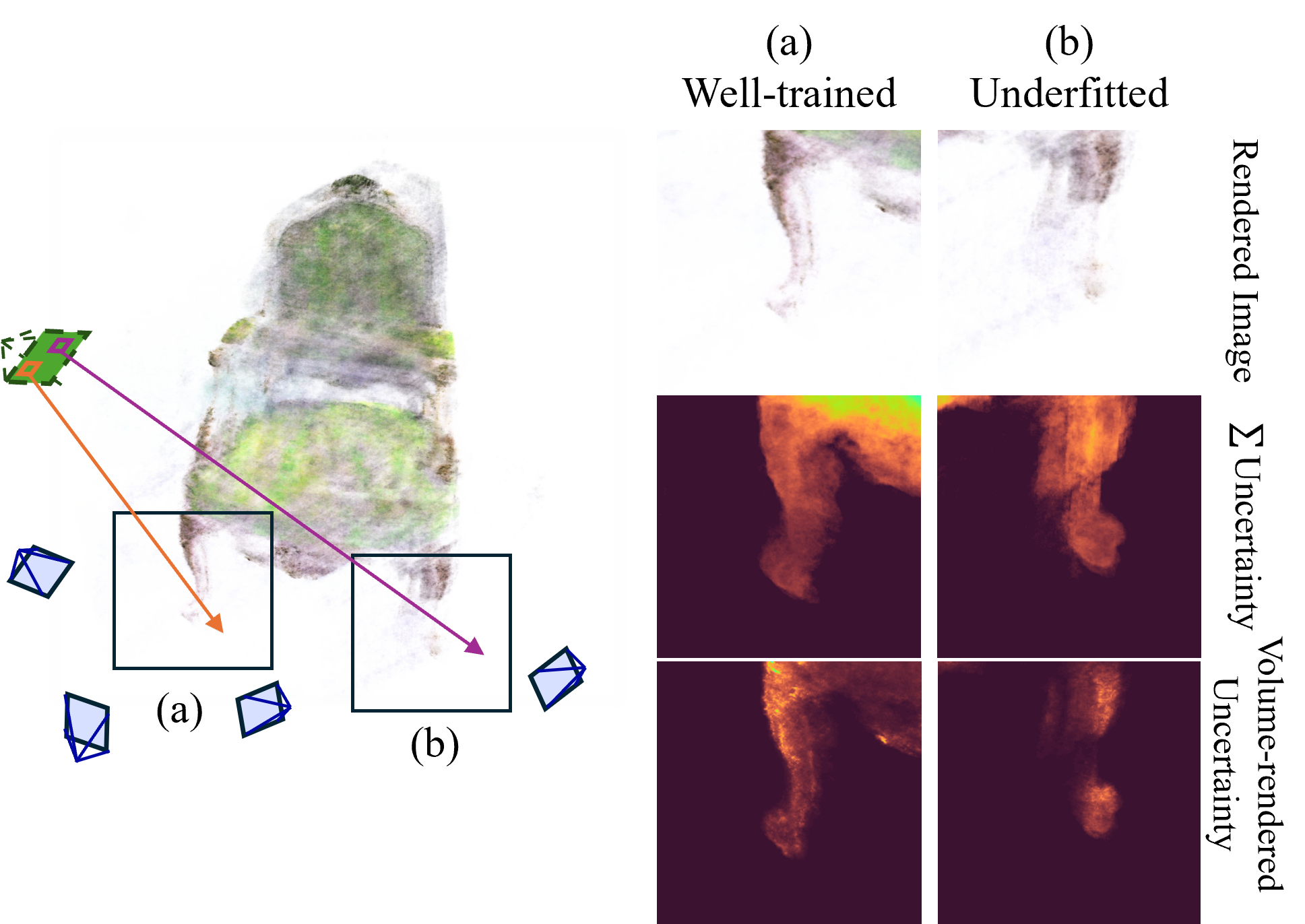
Surface-Based Visibility-Guided Uncertainty for Continuous Active 3D Neural Reconstruction
Hyunseo Kim, Hyeonseo Yang, Taekyung Kim, YoonSung Kim, Minsu Lee, Jin-Hwa Kim and Byoung-Tak Zhang
AAAI 2026 Artificial Intelligence with Biased or Scarce Data workshop Oral [pdf] [code]
Hyunseo Kim, Hyeonseo Yang, Taekyung Kim, YoonSung Kim, Minsu Lee, Jin-Hwa Kim and Byoung-Tak Zhang
AAAI 2026 Artificial Intelligence with Biased or Scarce Data workshop Oral [pdf] [code]
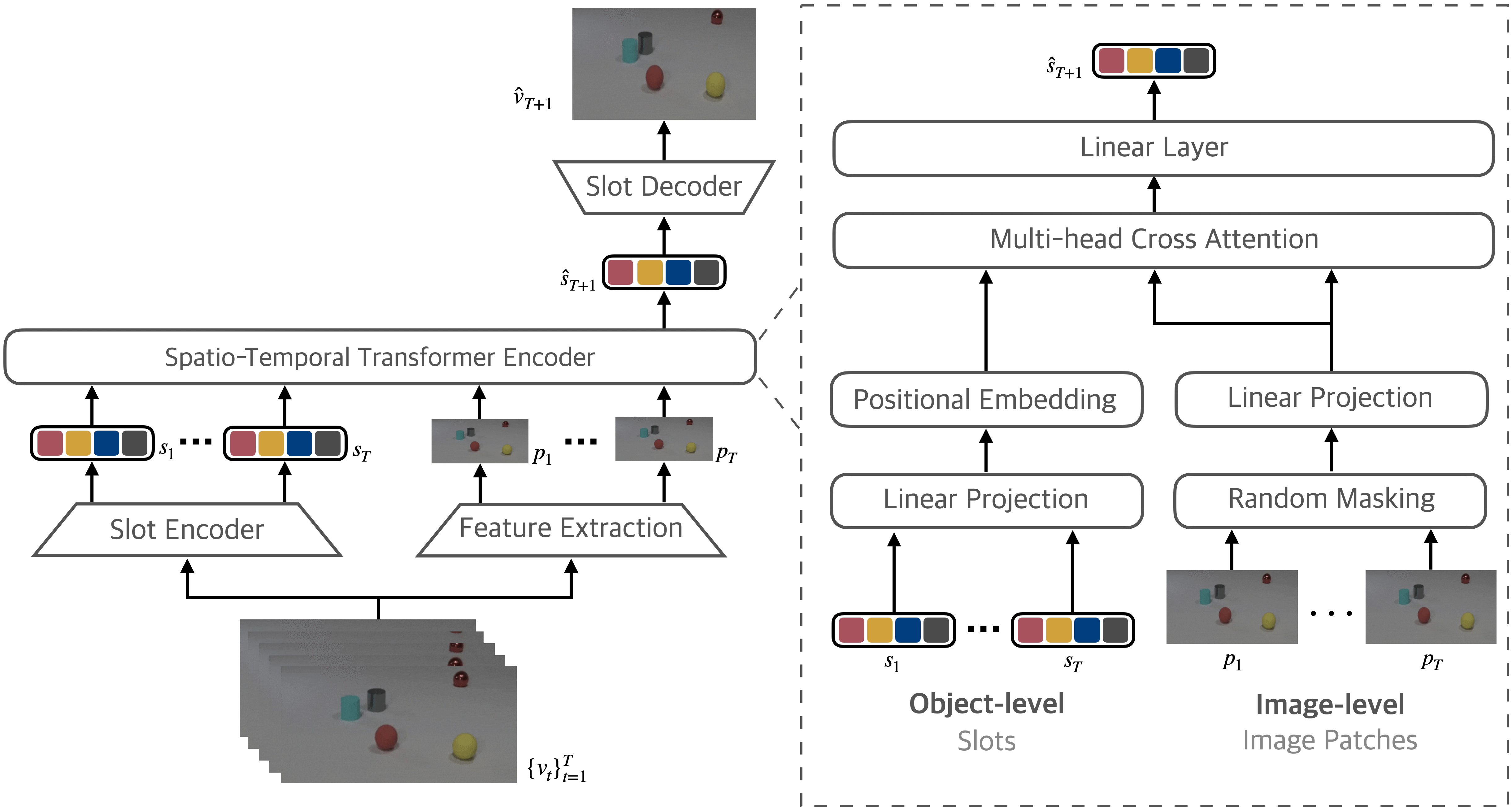
Learning Object Motion and Appearance Dynamics with Object-Centric Representations
Yeon-Ji Song, Hyunseo Kim, Suhyung Choi, Jin-Hwa Kim and Byoung-Tak Zhang
Causal Representation Learning Workshop at Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2023 [pdf]
Yeon-Ji Song, Hyunseo Kim, Suhyung Choi, Jin-Hwa Kim and Byoung-Tak Zhang
Causal Representation Learning Workshop at Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2023 [pdf]
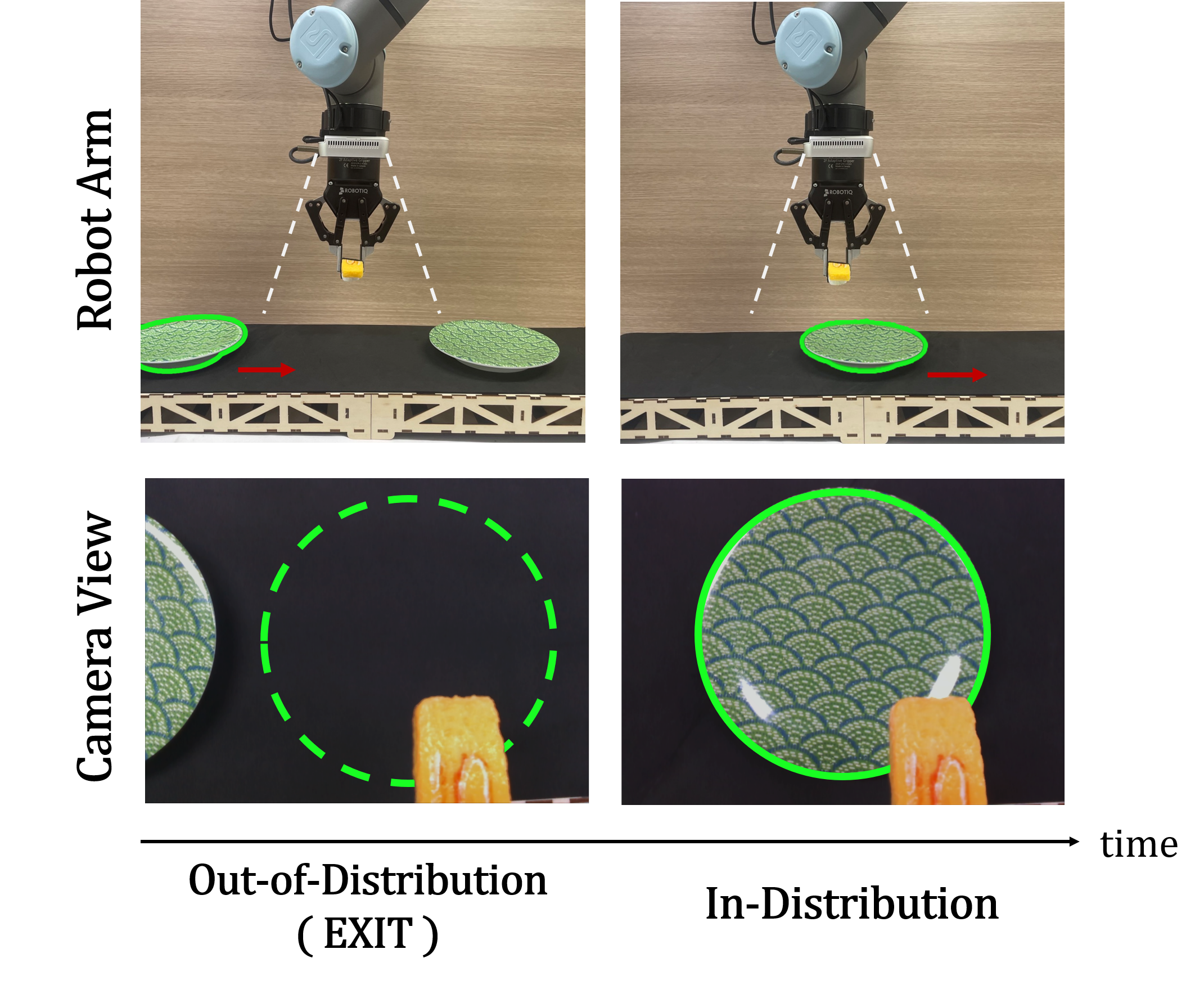
EXOT: Exit-aware Object Tracker for Safe Robotic Manipulation of Moving Object
Hyunseo Kim, Hye Jung Yoon, Minji Kim, Dong-Sig Han and Byoung-Tak Zhang
ICRA 2023 (acceptance ratio: 1345/3125~43%) [pdf] [code]
Hyunseo Kim, Hye Jung Yoon, Minji Kim, Dong-Sig Han and Byoung-Tak Zhang
ICRA 2023 (acceptance ratio: 1345/3125~43%) [pdf] [code]
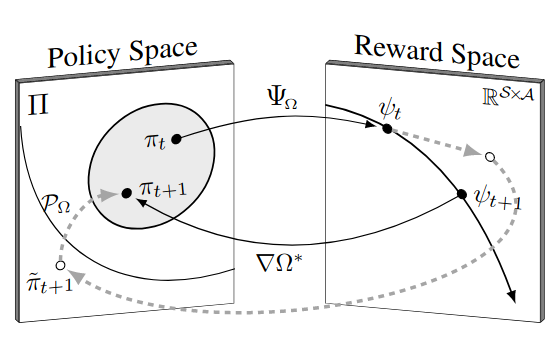
Robust Imitation via Mirror Descent Inverse Reinforcement Learning
Dong-Sig Han, Hyunseo Kim, Hyundo Lee, Je-Hwan Ryu and Byoung-Tak Zhang
NeurIPS 2022 (acceptance ratio: 2671/10411~25.66%) [pdf] [code]
Dong-Sig Han, Hyunseo Kim, Hyundo Lee, Je-Hwan Ryu and Byoung-Tak Zhang
NeurIPS 2022 (acceptance ratio: 2671/10411~25.66%) [pdf] [code]
Message Passing Adaptive Resonance Theory for Online Active Semi-supervised Learning
Taehyeong Kim, Injune Hwang, Hyundo Lee, Hyunseo Kim, Won-Seok Choi, Joseph J Lim and Byoung-Tak Zhang
ICML 2021 (acceptance ratio: 1183/5513~21.46%) [pdf]
Taehyeong Kim, Injune Hwang, Hyundo Lee, Hyunseo Kim, Won-Seok Choi, Joseph J Lim and Byoung-Tak Zhang
ICML 2021 (acceptance ratio: 1183/5513~21.46%) [pdf]
Label Propagation Adaptive Resonance Theory for Semi-Supervised Continuous Learning
Taehyeong Kim, Injune Hwang, Gi-Cheon Kang, Won-Seok Choi, Hyunseo Kim and Byoung-Tak Zhang
ICASSP 2020 (acceptance ratio: 1922/3939~47.2%) [pdf]
Taehyeong Kim, Injune Hwang, Gi-Cheon Kang, Won-Seok Choi, Hyunseo Kim and Byoung-Tak Zhang
ICASSP 2020 (acceptance ratio: 1922/3939~47.2%) [pdf]
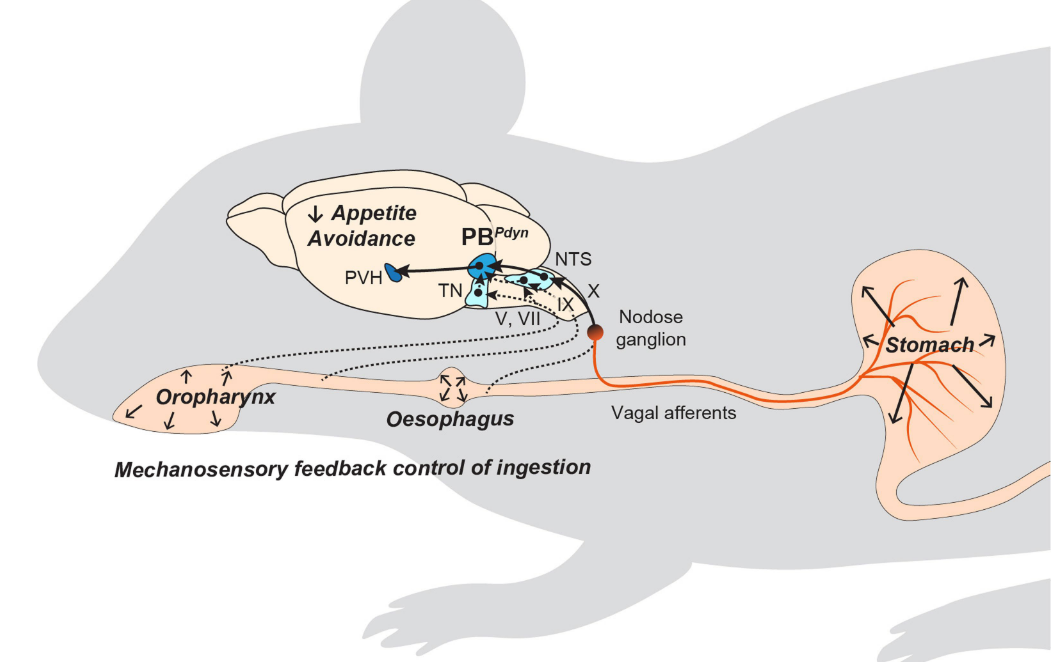
A neural circuit mechanism for mechanosensory feedback control of ingestion
Dong-Yoon Kim*, Gyuryang Heo*, Minyoo Kim*, Hyunseo Kim, Ju Ae Jin, Hyun-Kyung Kim, Sieun Jung, Myungmo An, Benjamin H Ahn, Jong Hwi Park, Han-Eol Park, Myungsun Lee, Jung Weon Lee, Gary J Schwartz and Sung-Yon Kim
Nature 2020 (acceptance ratio: ~7%) [pdf]
Dong-Yoon Kim*, Gyuryang Heo*, Minyoo Kim*, Hyunseo Kim, Ju Ae Jin, Hyun-Kyung Kim, Sieun Jung, Myungmo An, Benjamin H Ahn, Jong Hwi Park, Han-Eol Park, Myungsun Lee, Jung Weon Lee, Gary J Schwartz and Sung-Yon Kim
Nature 2020 (acceptance ratio: ~7%) [pdf]
Domestic Conference
Refined Object Tracking deducing Exit and Entrance signal with Large Multimodal ModelHyunseo Kim and Byoung-Tak Zhang
Proc. Korea Computer Congress 2024 (KCC 2024)
Bottleneck-Aware Linear Augmentation for Robotic Imitation Learning
Minji Kim, Ganghun Lee, Hyunseo Kim, Minsu Lee and Byoung-Tak Zhang
Proc. Korea Computer Congress 2024 (KCC 2024)
Self-Playing Reinforcement Learning Framework for Starcraft 2 Mini-Game
Moonhoen Lee, Hyunseo Kim, Minji Kim, Juno Kim, Hye Jung Yoon and Byoung-Tak Zhang
Proc. Korea Software Congress 2023 (KSC 2023)
Future State Generation for Action Prediction in Cross Domain
Hyunseo Kim, Yu-Jung Heo, Kibeom Kim and Byoung-Tak Zhang
Proc. Korea Computer Congress 2021 (KCC 2021)
Predicting health indicator using Vector autoregression
Hyunseo Kim, Won-Seok Choi and Byoung-Tak Zhang
Proc. Korea Software Congress 2019 (KSC 2019)
Patents
움직이는 물체를 조작하는 로봇을 위한 물체 추적 장치 및 방법장병탁, 김현서, 윤혜정, 김민지, 한동식
대한민국 특허, 출원번호 10-2023-0067656
PCT, 출원번호 PCT/KR2023/011511
Last update: September 2025 by Hyunseo Kim